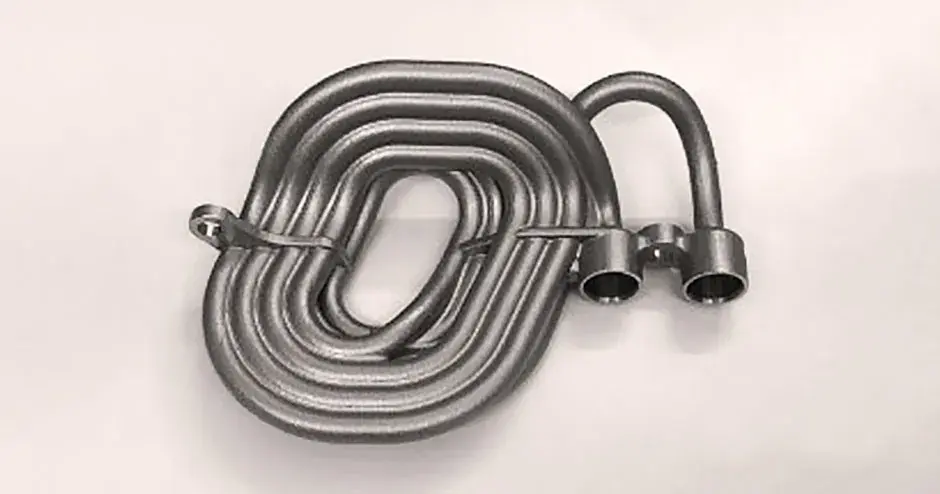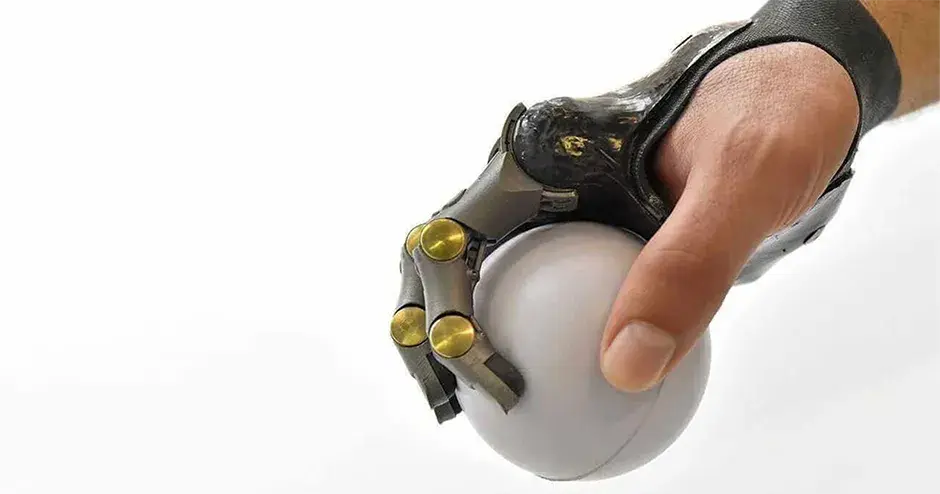
What is Direct Metal Printing?
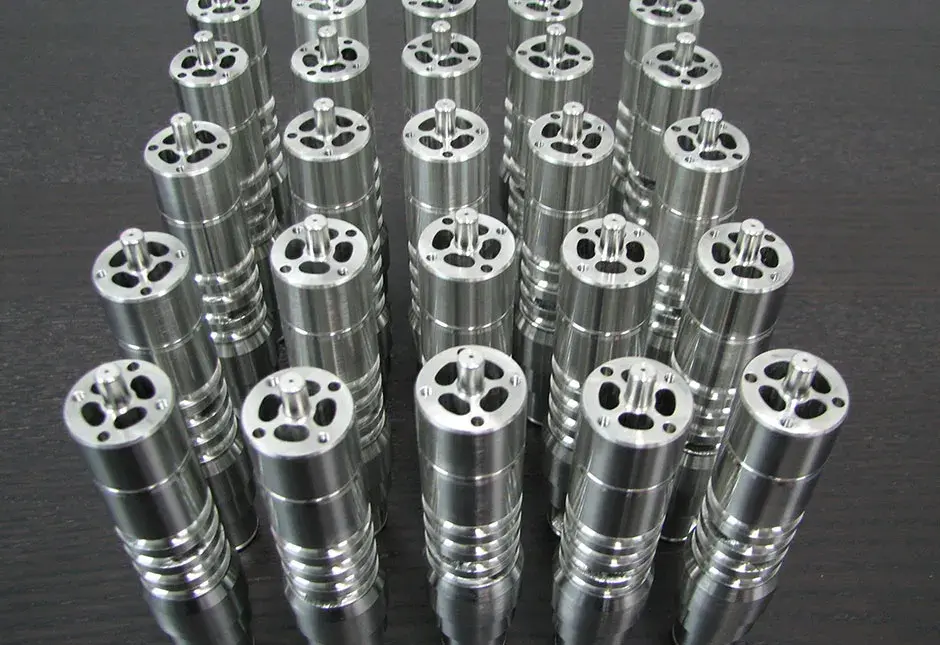
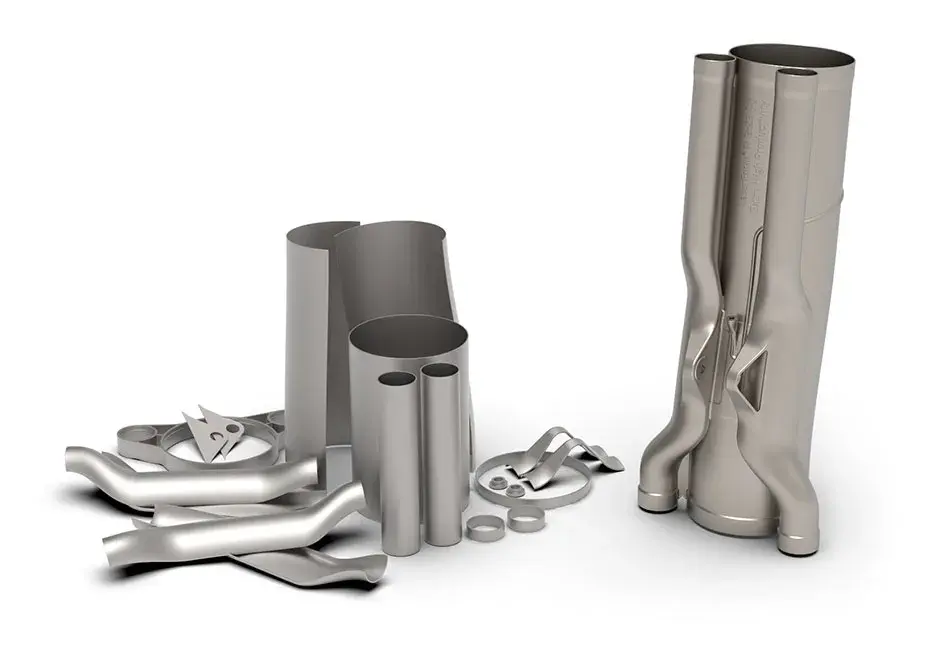
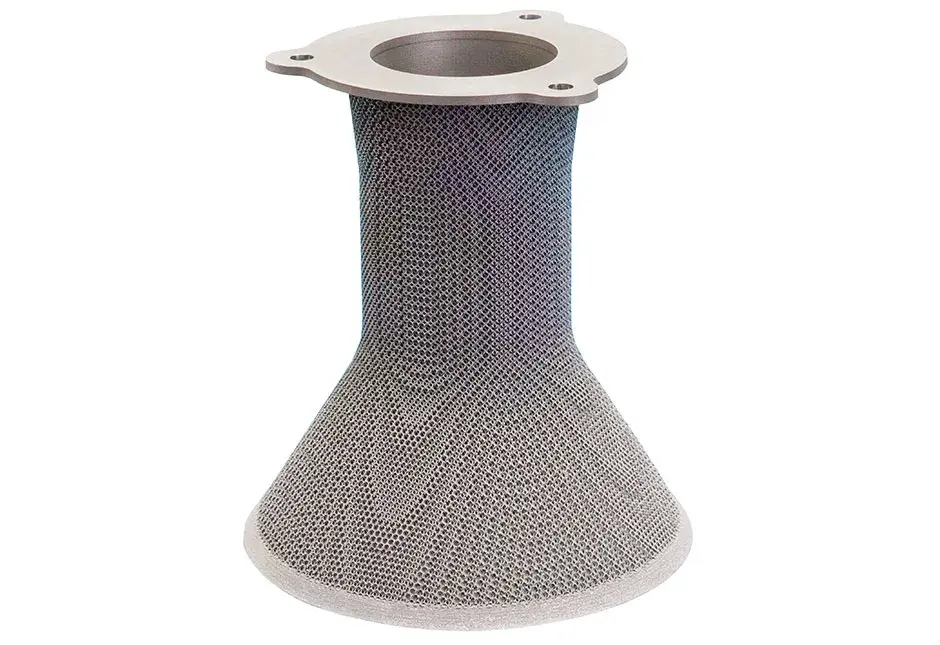
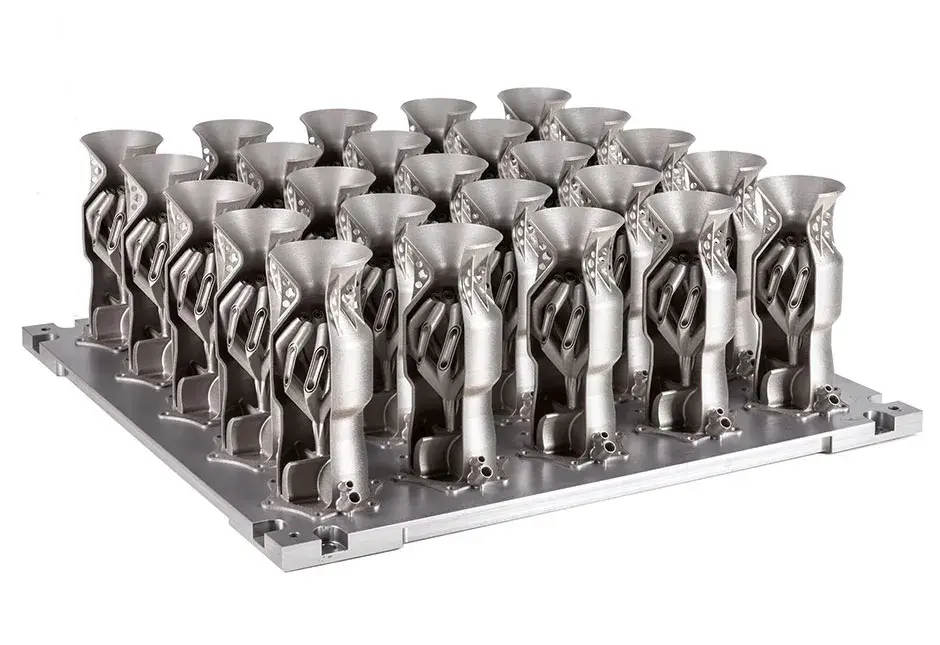
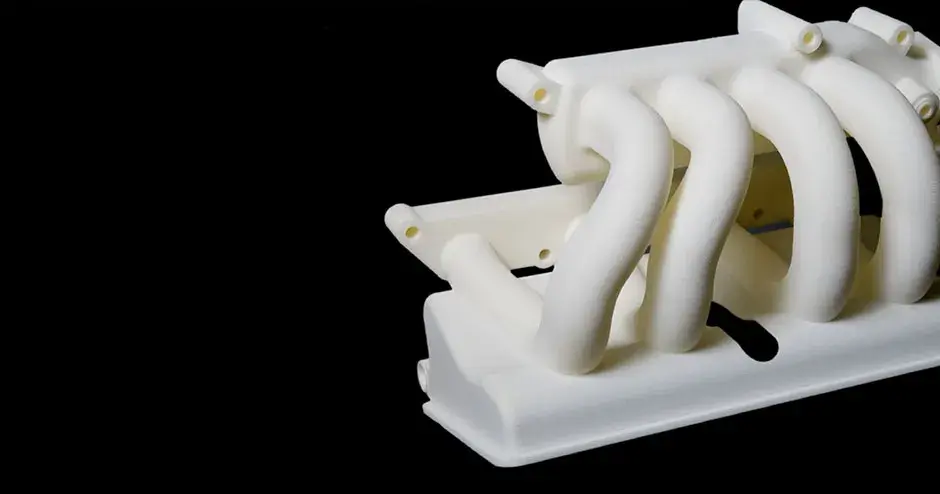
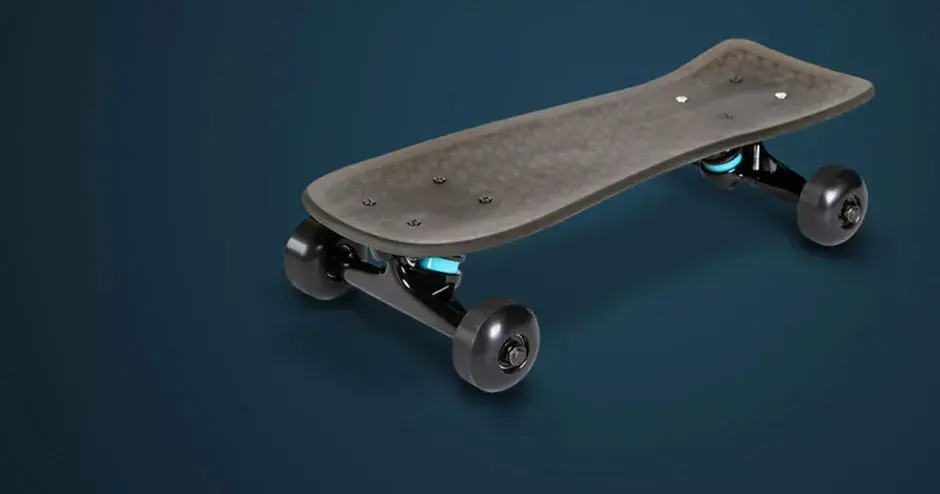
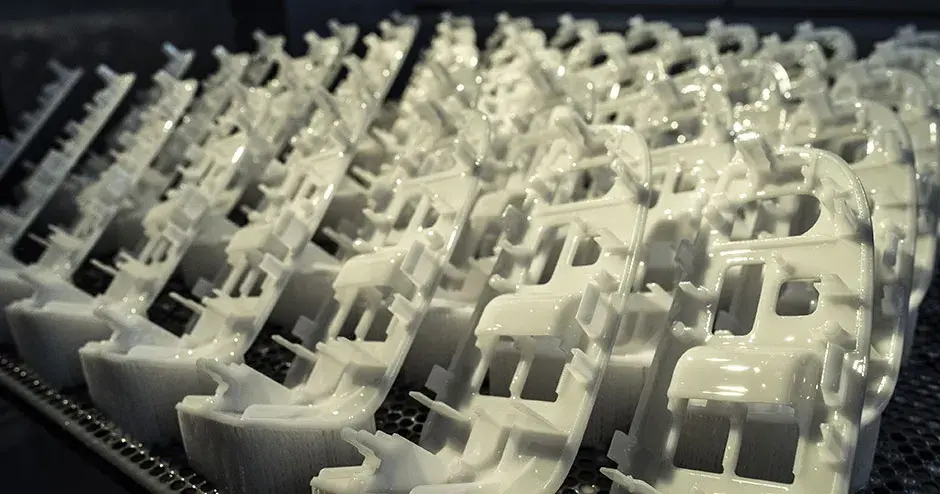
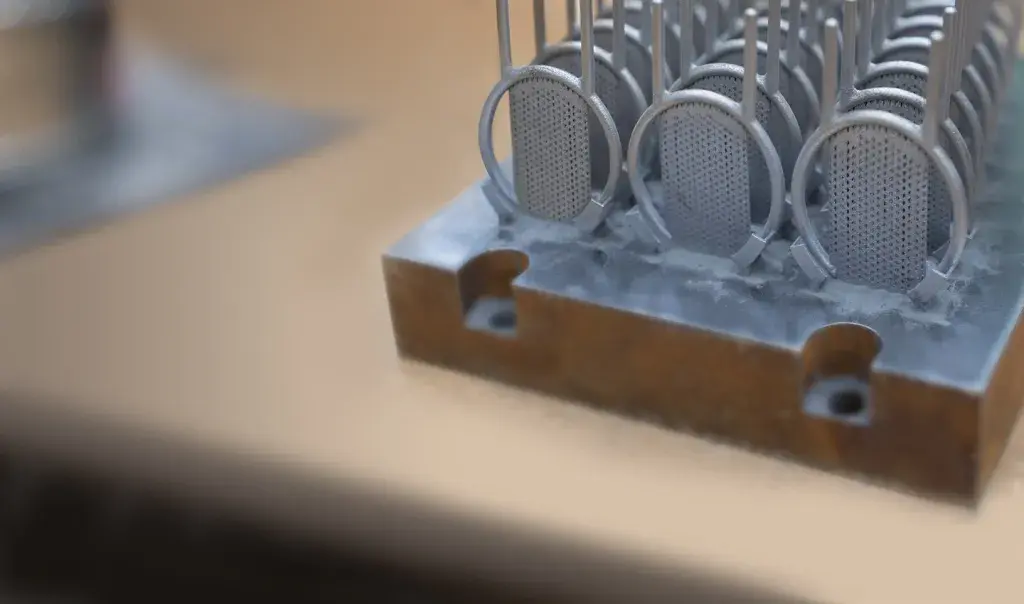
Direct metal printing (DMP), also commonly known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), is an additive manufacturing technology that builds high quality complex metal parts from 3D CAD data. In the machine, a high precision laser is directed to metal powder particles to selectively build up thin horizontal metal layers one after the other. This cutting edge technology allows for the production of metal parts with challenging geometries, not possible using traditional subtractive or casting technologies. A variety of functional metals are available to print designs, from prototypes to production series of up to 20,000 units.